
We are here to support you and your family during this time of transition.
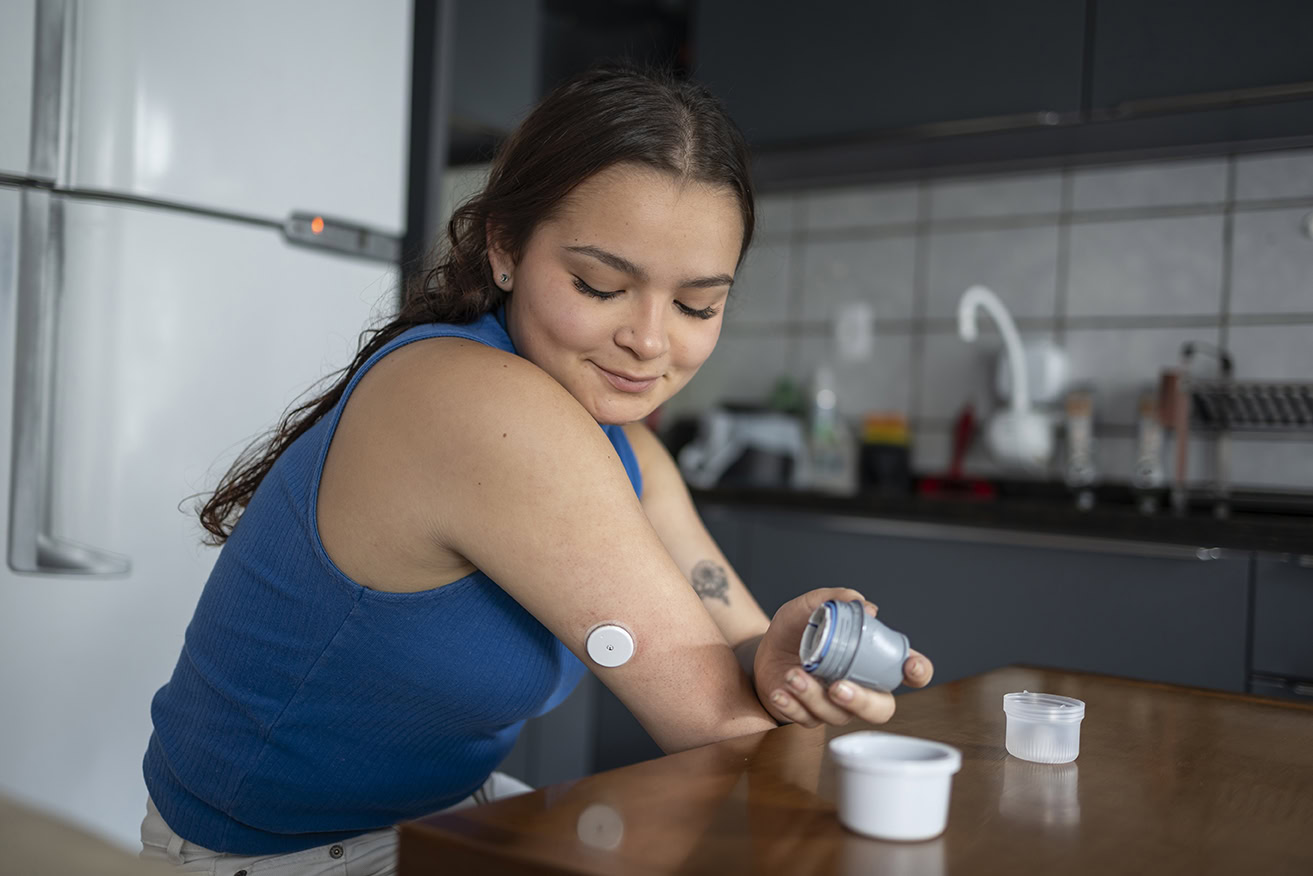

In T1D, the body’s immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Insulin is an essential hormone that helps the body turn food into energy. People living with type 1 diabetes must take insulin by injection or insulin pump to survive.
Living with T1D requires extra work, but with the right support and information, you or your loved one can lead a full and healthy life.
The most common warning signs of type 1 diabetes are:
The onset of symptoms can be sudden, especially in young children. If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms, contact your medical provider immediately.
Diabetes is a disease that disrupts the body’s production of insulin, a hormone that regulates blood-sugar levels. Though they share some similarities, type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D) have different causes, effects, and treatments.
People living with T1D in the U.S.
People living with T1D globally
Americans living with T1D under the age of 20
Age range of most Americans living with T1D

Onset triggers associated with T1D
Tests that lead to a type 1 diabetes diagnosis
Therapies for treating T1D
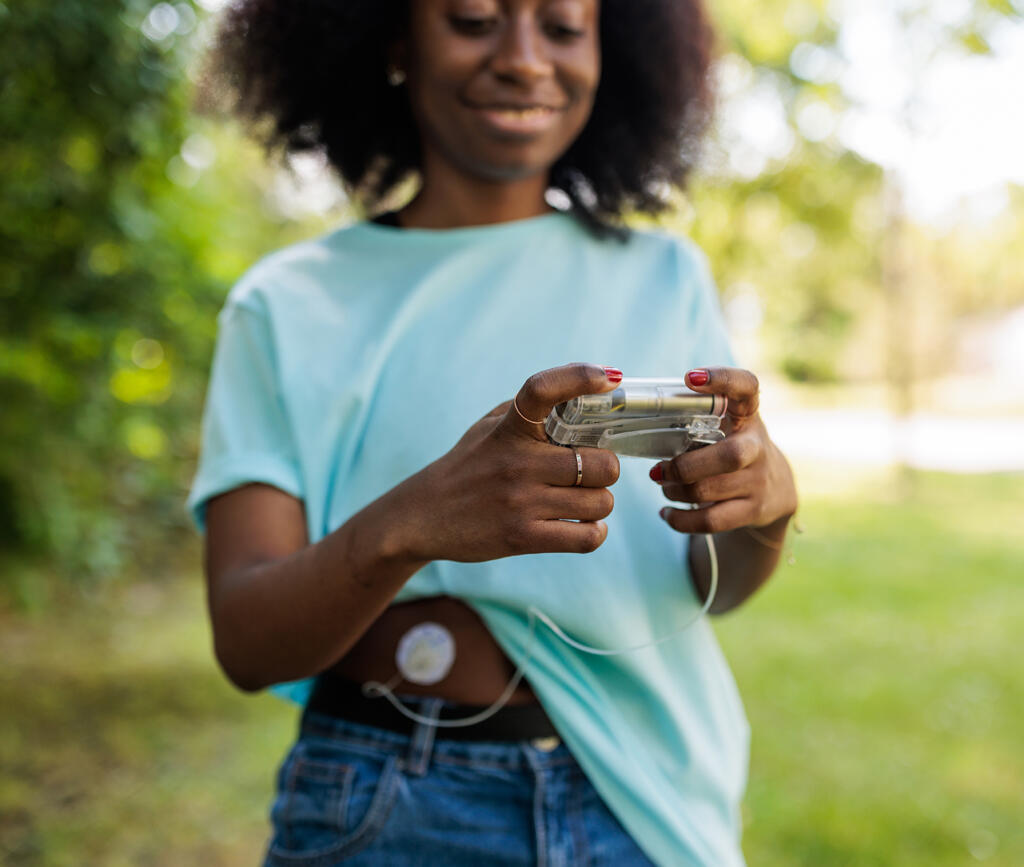
Types of insulin and administration methods
The science behind type 1 diabetes
Answers to your questions about type 1 diabetes
The global scope and impact of T1D
We’re all here because we’ve all been there.

We are here to support you and your family during this time of transition.
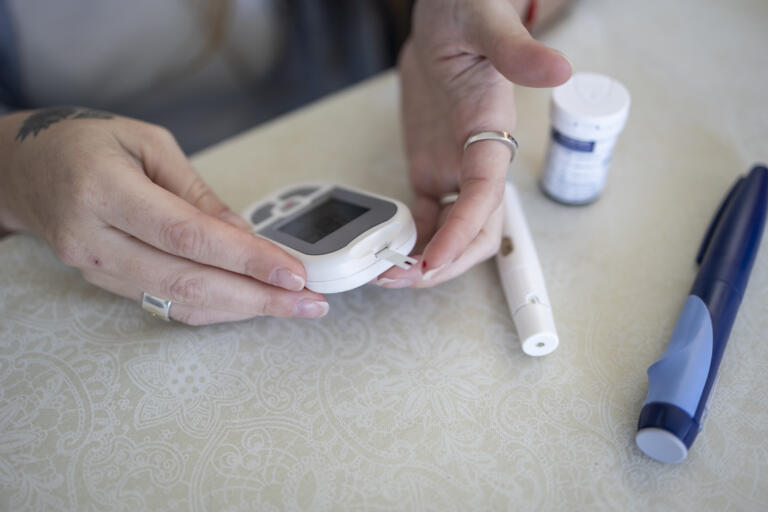
Learn about the tools, therapies, and technologies available to manage T1D.

Connect with your local chapter and learn more about in-person and virtual events.
Type 1 diabetes develops in stages over time. Detecting T1D in its early stages can prevent life-threatening complications. You may also be eligible for research studies to advance treatments and cures or FDA-approved therapies that delay the onset of T1D.